Astigmatism
Astigmatism causes all vision, near and far to be blurry.
Low astigmatic eyes have only a small blurr. But higher stigmatic eyes will experience extreme blur for all vision tasks.


Astigmatism causes night time elongated halos around lights.
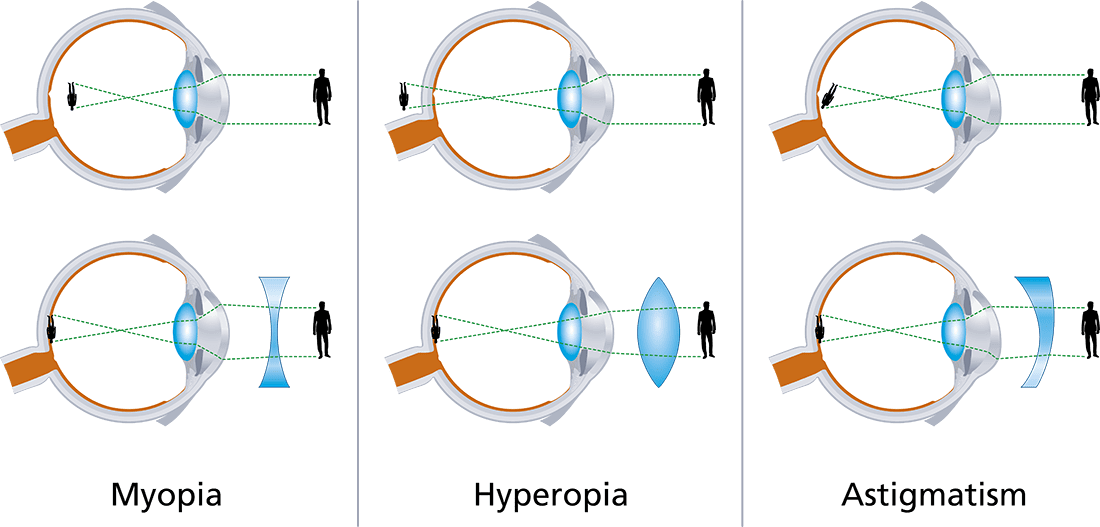
Eye focus problems and their spectacle or contact lens solutions.
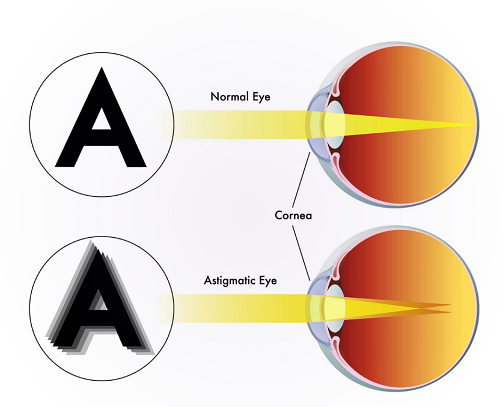
An astigmatic eye has two distinct powers ie. 1/-2 or -1/+2 and a location angle ie 75′ This cause several images to form inside the eye which in turn has transition blur ie. between -1.00 and +1.00 are countless different lens power which add to the blurr.
Astigmatism is a commonly known as a squint. It is a refractive error of the eye that results from an irregular shape of the cornea or eyes crystalline lens. Instead of being perfectly spherical, the cornea may be more oval(long egg surface)-shaped, leading to variations in how light is focused on the retina. This distortion causes blurred or distorted vision at various distances.
 The only natural way to see clearer is to squint.
The only natural way to see clearer is to squint.
Hence astigmatism is also called a squint.
Astigmatism is in most cases is a focus fine tuning mechanism. If you have 2dpt astigmatism you will see reasonably clearly also with a 1dpt lens. But your vision will not be as sharp. Medical astigmatism, which can change dramatically in power is called keratoconus and is often a rare congenital condition.
### Key Points About Astigmatism
1. **Causes**: The primary cause is the irregular curvature of the cornea or lens. It can also be influenced by genetic factors or can develop after eye surgery or injury.
2. **Symptoms**: Common symptoms include blurred vision, difficulty seeing at night, eye strain, headaches, and sometimes the perception of doubled images.
3. **Diagnosis**: An eye care professional diagnoses astigmatism through a comprehensive eye exam, which includes a refraction test and keratometry to measure the curvature of the cornea.
4. **Treatment**: Treatment options include corrective lenses (glasses or contact lenses) that compensate for the irregular curvature. In some cases, refractive surgery, like LASIK or crystalline cataract lens surgery may be an option to permanently reshape the cornea.
5. **Prevalence**: Astigmatism is quite prevalent and can occur in combination with other refractive errors like myopia (nearsightedness) or hyperopia (farsightedness).
Related rare medical astigmatism
- A very rare type of astigmatism is a genetic progressive medical disease called Keratoconus . It causes the eye to bulge and the vision to become an irregular form astigmatism. Corneal grafts are frequently required to halt the growth.

- Astigmatism can also appear after eye trauma or surgery. When an eye heals with misalignments an irregular astigmatism can occur. If the scar is on the outside of the cornea contact lenses may help. Because the contact lens fluid between the cornea and the hard contact lens become an lens that adapt water line to the irregular cornea.
- Astigmatic cataract patient might still have astigmatism after cataract surgery.
- After a difficult very invasive cataract surgery astigmatism can occur during the healing process.
By understanding astigmatism, individuals can seek appropriate treatment to improve their visual clarity and comfort. Regular eye exams are essential for early detection and management.
Hyperopia

Hyperopia, commonly known as farsightedness, is a refractive error of the eye where distant objects may be seen more clearly than nearby ones. This condition occurs when the eyeball is too short relative to the focusing power of the cornea and lens, or when the curvature of the cornea is too flat. As a result, light entering the eye is not focused accurately on the retina, causing blurred vision for close objects.
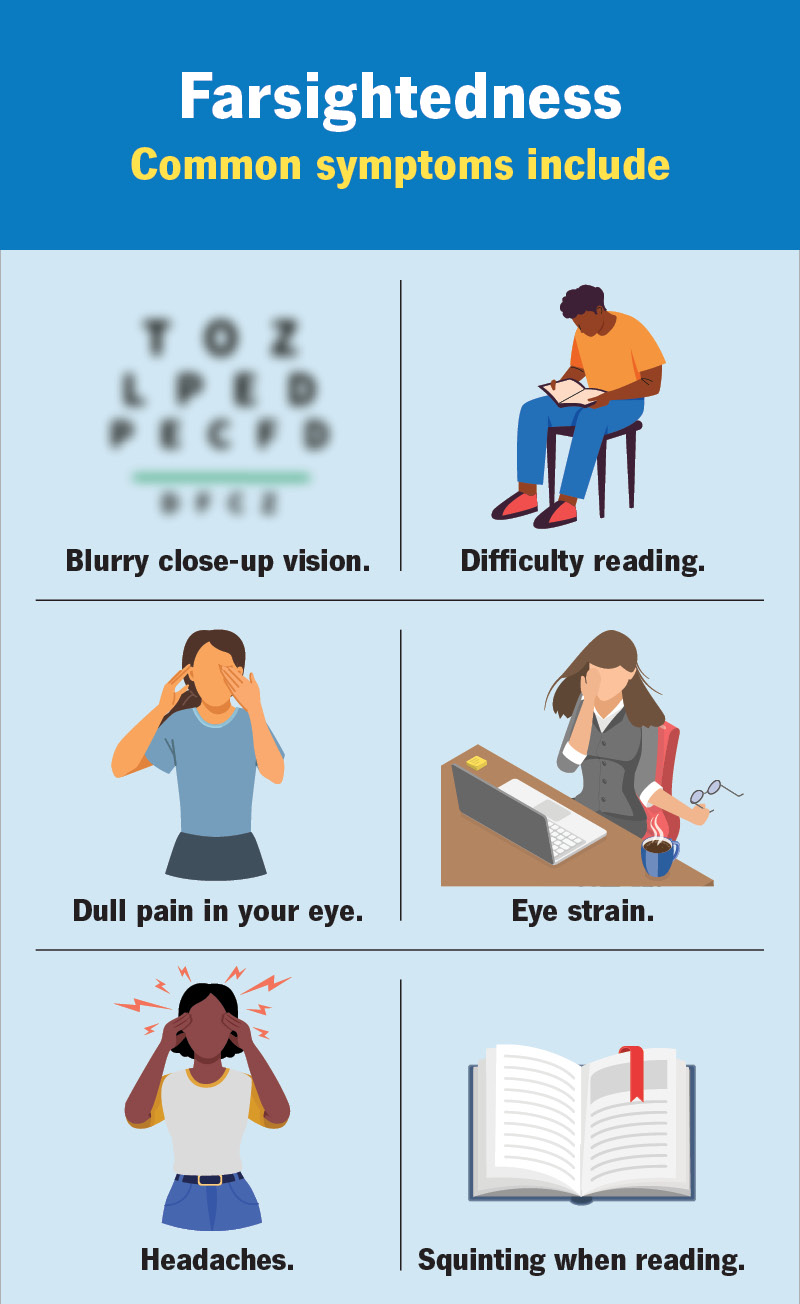
Symptoms
– Blurred vision for near tasks like reading or sewing.
– Eye strain, especially during prolonged focus on close objects.
– Headaches.
– Difficulty with contrasting images.
Diagnosis
An eye care professional can diagnose hyperopia through a comprehensive eye examination, which may include:
– Visual acuity tests.
– Refraction tests to determine prescription needs.
Treatment
– **Eyeglasses or Contact Lenses**: Convex lenses are prescribed to help refract light onto the retina more effectively.
– **Refractive Surgery**: Procedures such as LASIK or PRK can reshape the cornea to improve focus.
– **Vision Therapy**: In some cases, exercises may be recommended to strengthen eye muscles.
Management
Regular eye exams are important, especially for children, as untreated hyperopia can lead to crossed eyes or other vision issues. Managing the condition effectively can improve quality of life and visual comfort.
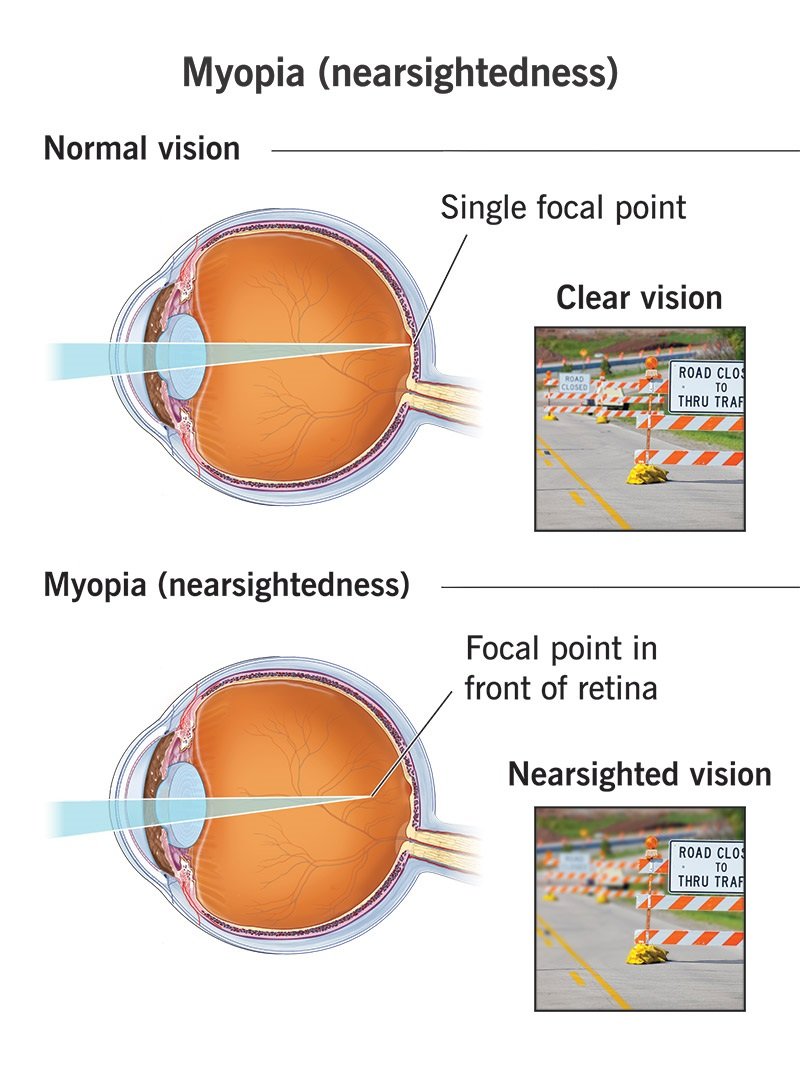
Myopia

Myopia, commonly known as nearsightedness, is a refractive error of the eyes that causes distant objects to appear blurry while close objects can be seen clearly. This condition occurs when the eyeball is too long or the cornea has too much curvature, preventing light from focusing directly on the retina. The eyes focus system is simply tro strong in power. IF you wonder what is feels like to be myopic. Just look through a magnifier. Close objects will be clear and distant object blurry.
Symptoms
– Difficulty seeing distant objects, such as road signs or the board in classrooms.
– Eye strain or discomfort, especially after prolonged concentrated distance vision tasks.
– Needing to sit closer to screens or the front of a classroom.
– Holding reading materials closer than normal sighted people.
– **Genetic Factors**: A family history of myopia increases the likelihood of developing the condition.
– **Environmental Factors**: Spending extensive time on close-up tasks (like reading or using screens) and limited outdoor activity can contribute to its development.
Can myopia be fixed or modified?
This is a sticky topic and the answer is:
- Yes temporarily or partially through surgery.
- Cornea reshaping can reduce myopia as long as the corneas thickness allows this procedure. In cases of very high myopia it can only reduce the myopia prescription and not eliminate it. Reducing a high myopic prescription brings no advantages to a MYOPE:
- The eyes crystalline lens can be removed and replaced with a weaker lens that hopefully focuses clearly on the retina. But impants need to be of a multicical or monofocal type. Monofocal allows better clarity and can be fine-tuned with mild prescription glasses.
- Temporarily and anecdotally, myopic progressions can be retarded by wearing weaker spectacle lenses for reading. This works best whilst the eye is growing and mostly under the supervision of an optometrist. In some countries the military sponsors this method because epidemiologically myopic cases are growing rapidly because of the use of cellphones. Wearing small + glasses is anecdotally a suitable way to ensure that more soldiers do not require myopic distance glasses.
Advantages of Myopia
Better Near Vision: Individuals with myopia can see nearby objects sharply, which can be advantageous for tasks such as reading, sewing, or other close-up work.
Less Strain for Near Activities: Myopic individuals might experience less eye strain during activities that involve focusing on things at a close range, as their eyes naturally focus better for these distances.
Enhanced Creativity in Certain Professions: Some studies suggest that myopia is more common among individuals in academic or creative fields, possibly due to prolonged close-up work. This correlation may lead to advantages in areas that require detailed visual work.
- When myopes after 40 do rarely need reading glasses. they simply take off their distance glasses.
Disadvantages of Myopia
Difficulty Seeing Distant Objects: The primary disadvantage is that individuals struggle to see objects that are far away, which can impact activities like driving or participating in sports.
Increased Risk of complicating some medical Eye Conditions: Myopia can lead to an increased risk of serious eye disorders, including glaucoma, retinal detachment in cases of extremely high myopia..
Dependence on Corrective Lenses: Many myopic individuals need to wear glasses or contact lenses, which can be inconvenient and expensive. It may also be challenging for those who prefer not to wear corrective eyewear.
Progressive Nature: For many, myopia can worsen over time, leading to more severe vision problems and requiring stronger prescriptions.
Emotional and Social Implications: In some cases, once glasses or contacts are required, individuals may experience feelings of self-consciousness or social anxiety, especially if they face difficulties in activities like sports or public speaking.
Conclusion
While myopia offers some benefits, particularly in tasks that require clear near vision, the overall disadvantages, particularly concerning safety and long-term eye health, outweigh these advantages in cases of high myopia (over about -8dpt). Regular eye exams and appropriate interventions, such as corrective lenses or vision therapy, are common tools for managing myopia effectively.